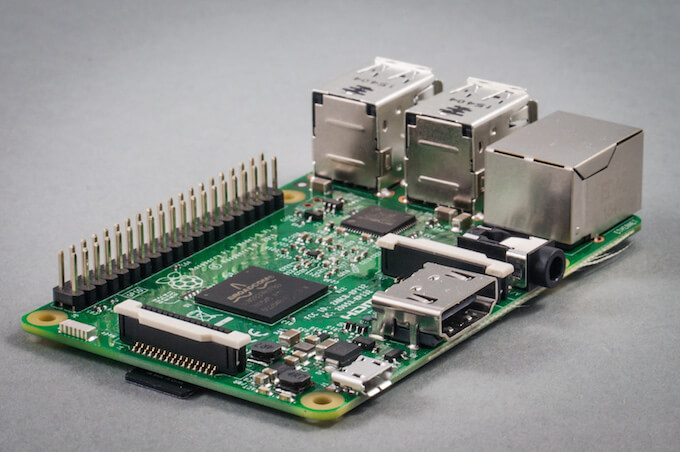
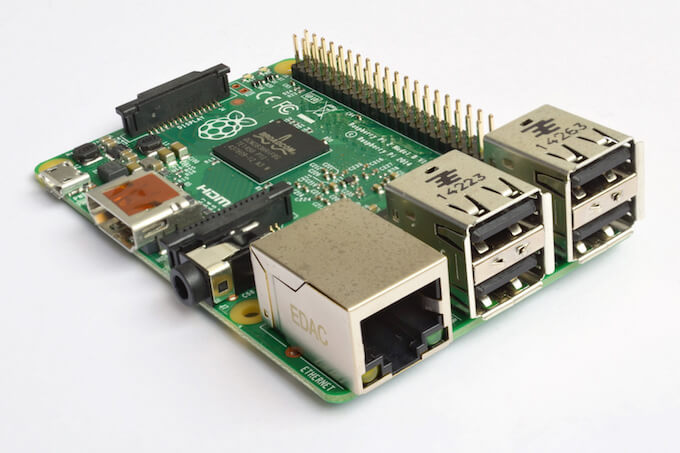
Raspberry Pi 3 is a credit -card sized powerful and low cost mini computer. If you have not gone through its specifications yet, check out our previous post on Raspberry Pi 3 Specifications and Features. Assuming you know of it, I surely believe you are interested in Raspberry Pi 3, isn’t? Wait, ODROID C2, is an alternative to Raspberry Pi 3 that is released in March 2016 and offers more power and in the same price range. There is a long debate about ODROID C2 putting Raspberry Pi 3 on the ropes. Let us see.
By March 2016 the project Raspberry Pi Foundation has completed 4 years. In this short time it has managed to put into the market more than 8 million Raspberry Pi (and 10 Million Raspberry Pi sales completed by September 2016). It is true that this minicomputer is the most popular and has a huge community behind. But this doesn;t mean they are the only ones present. This article brings to light ODROID C2 which one such minicomputer which could dethrone Raspberry Pi 3 in the near future.
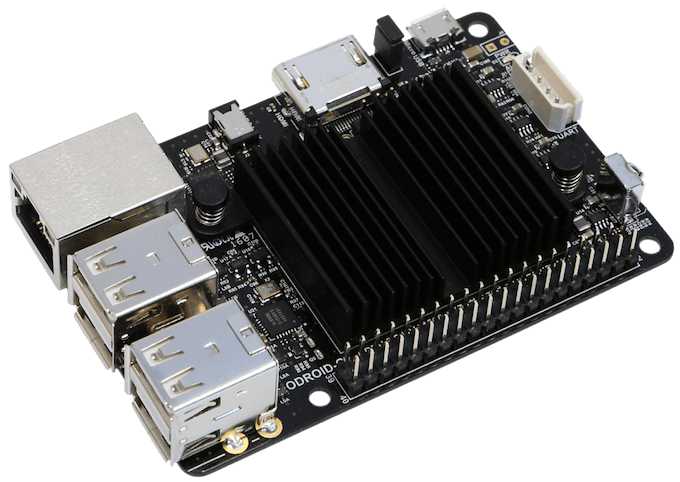
ODROID C2 is the product of a company called Hardkernel. This is the company behind many electronic components from boards to camera modules or adapters. It’s C2 board is a worthy rival for the Raspberry Pi 3 and has even surpassed it in some sections.
Features of ODROID C2
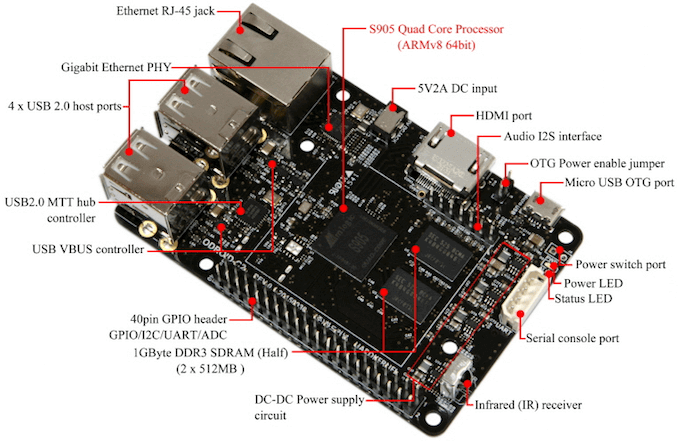
At the heart of ODROID C2 is a Amlogic S905 SoC with a quad – core ARM Cortex A53 CPU. Though the BCM2837 of Raspberry Pi 3 has the same quad core processor, its clock speed of 1.2GHz is lower compared to the 2GHz clock speed in ODROID C2.
Even in the section of memory, the Hardkernels’ ODROID C2 scores better with 2GB of DDR3 RAM. While in Raspberry Pi 3 there is only 1GB DDR2 RAM which disappointed many enthusiasts at its launch itself. This is because users have started to exploit the minicomputer more and the 1GB DDR2 RAM is no longer sufficient.
Another point where the ODROID C2 leads the Raspberry Pi 3 is the Gigabit Ethernet port. However, the lack of integrated Bluetooth and WiFi connectivity is a negative for the ODROID C2. Hence you will have to keep using those USB Adaptors to get your board up and connect to the network.
Price and additional features
There are other like the HDMI port that supports 4K signal, built-in analog to digital convertor. ODROID C2 can run the Ubutu 16.04 or the Android Lollipop operating system. Despite all these additional features and many other boards posing as Pi killers, the fact that the ODROID C2 offers all this at a price of only $ 15 more is quite interesting. While the Raspberry Pi 3 costs $ 35, the C2 costs $ 50.
So which board will you prefer to buy? Raspberry Pi 3? or ODROID C2? Before you make up your mind, here’s one last important point. The Raspberry Pi Foundation has a vast online community with many developers working on it world-wide. We have previously collected several Raspberry Pi FAQs to help you get started right away.
In case you are a beginner you might want to consider the fact that the Hardkernal’s prototyping community is yet to build. Though the company looks ambitious to increase it with several other boards in the line-up the support you get right away is questionable. But if you are experienced using the Raspberry Pi 3 then there’s no reason why you shouldn’t get a ODROID C2 at the earliest and help build the community.
Image Credits: Hardkernal